Coconut Oil vs. Fish Oil
Coconut oil and fish oil have little in common, except that they are both healthy sources of dietary fat. They are quite different in their properties and in the way that they are incorporated into the diet. Now that the low fat craze is ending, these oils are becoming popular additions to a healthful diet. Fish oil is one of the healthiest animal fats, but natural sources are, unfortunately, disappearing from our food supply. The more abundant coconut oil is one of the healthiest plant fats, and has a long history of use in many traditional food-ways.
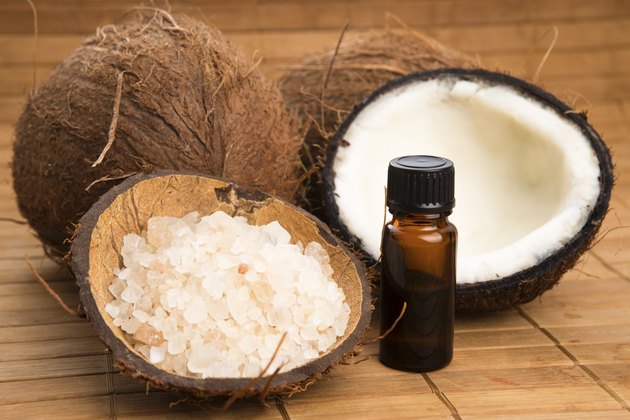

Coconut Oil
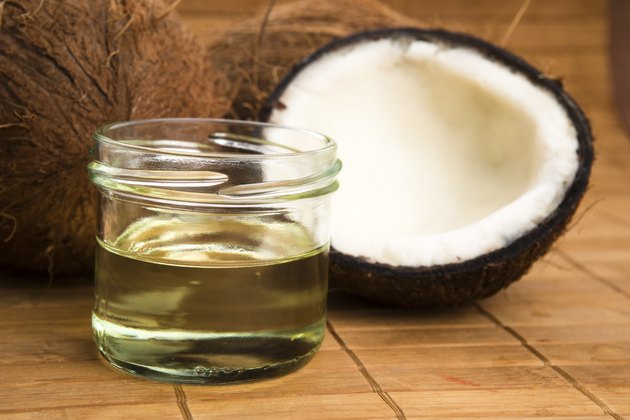

Coconut oil is a source of beneficial saturated fatty acids. It contains two medium-chain saturated fatty acids — lauric acid and caprylic acid — that are especially good for your health. A study published in the “Journal of Medicinal Food” in 2013 showed that coconut oil effectively treated an antibiotic-resistant bacteria called Clostridium Difficile. Medium-chain fatty acids may also help speed up fat-burning and help with weight loss, as demonstrated by a 1996 study in the “European Journal of Clinical Nutrition.”
Fish Oil
Fish oil is composed mostly of long-chain omega-3 fatty acids known as EPA and DHA. A great source of omega-3s is oily coldwater fish, such as salmon, mackerel, tuna and sardines. Unfortunately, some of these, especially wild salmon, are becoming less plentiful and may be contaminated with environmental pollutants. Purified fish oil capsules might be a better source. EPA from fish oil is anti-inflammatory, which could be helpful in preventing cardiovascular disease, according to “Cardiology in Review.” DHA is part of healthy brain tissue, and according to a 2011 study published in the “Journal of Clinical Psychiatry,” might even help alleviate mental depression.
Compare and Contrast

Coconut oil and fish oil differ in how they are used and stored. Coconut oil is stable and has a long shelf life. Its medium-chain saturated fatty acids cause it to be solid at cold temperatures and semi-soft at room temperature. It is great for cooking because the saturated fatty acids are resistant to being damaged by high heat. The fatty acids in fish oil are polyunsaturated, which means that they are fragile and are easily oxidized upon exposure to air or prolonged high temperatures. A jar of coconut oil can be kept at room temperature without deteriorating, but fish oil will quickly become rancid if not refrigerated and protected from air, which eliminates its health benefits.
Other Considerations

Regular consumption of fresh, high quality fish oil helps to keep the arteries properly dilated and the blood at a proper consistency. Some people, especially vegans, prefer to get their omega-3’s from flax seed oil. However, the omega-3 fatty acids in flax seed must be converted into EPA and DHA in the body, which may not be very efficient, according to Harvard Medical School. Substitute coconut oil for ordinary vegetable oil for cooking. Most vegetable oils are rich in a different type of polyunsaturated fatty acid than those in fish oil, known as omega-6 fatty acids. Although they are not quite as fragile as omega-3’s, they do become damaged at cooking temperatures.


